Topic: Defferentiation And Embryonic Development
Defferentiation And Embryonic Development
Following fertilization, a zygote divides and soon becomes a multicelled embryo with many different cell types, as represented below.
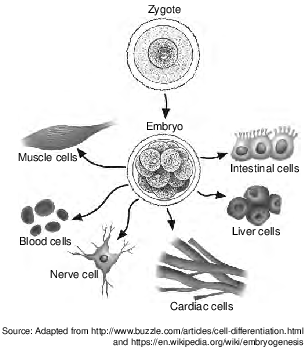
Which statement best explains this development?
(1) Specialization occurs, resulting in the formation of a great variety of cell types.
(2) Genes are inserted into the zygote to allow for the formation of different cell types.
(3) The expression of genes responsible for the different cell types is controlled by the placenta.
(4) The genetic information in the zygote is divided to produce a complete set for each cell type.
Which process allows a mammal to continue to grow in size?
(1) mitosis of sex cells
(2) mitosis of body cells
(3) meiosis of sex cells
(4) meiosis of body cells
A zygote develops into a multicellular organism through
(1) mitosis and specialization
(2) mitosis and meiosis
(3) recombination and communication
(4) genetic engineering and natural selection
Some plants increase in height due to changes in specialized regions of cells in the tips of their branches. The processes that result in these changes include
(1) meiosis, cell growth, and cloning
(2) mitosis, zygote formation, and cloning
(3) meiosis, gamete formation, and differentiation
(4) mitosis, cell growth, and differentiation
For a human zygote to become an embryo, it must undergo
(1) fertilization
(2) recombination
(3) meiotic divisions
(4) mitotic divisions

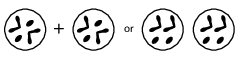
Which process takes place in both method A and method B?
(1) meiosis
(2) mitosis
(3) fertilization
(4) recombination

A process that could be represented by A is
(1) fertilization
(2) meiosis
(3) mitosis
(4) mutation
DNA replication occurs in preparation for
(1) mitosis, only
(2) meiosis, only
(3) both mitosis and meiosis
(4) neither mitosis nor meiosis
After a zygote is formed, specialization of cells occurs. Through which process do the cells of a zygote become specialized?
(1) sexual reproduction
(2) meiosis
(3) fertilization
(4) differentiation
The development of organs and tissues from a zygote includes
(1) mitosis and differentiation
(2) mitosis and gamete production
(3) meiosis and gamete production
(4) meiosis and fertilization
Identify one way in which the process of growth of a human embryo is similar to the process of reproduction in a single-celled organism. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — They both involve mitosis.
• — Both processes produce cells containing identical genetic information.
• — The cells are produced asexually.
The diagram below represents a cell nucleus. Complete the diagram so that it shows the arrangement of the genetic material in the two new cells that are produced by mitosis. [1]

Allow 1 credit for completing the diagram as shown below.
• 
The Critical Role of the Placenta
The proper functioning of the placenta is critical to the growth and development of a healthy fetus. For example, the placenta appears to act as a nutrient sensor. It regulates the amounts and types of nutrients that are transported from the mother to the fetus.
Improper functioning of the placenta can alter the structure and function of specific cells and organ systems in the developing fetus, putting it at risk for health problems as an adult. For example, in some pregnancies, the placenta develops a resistance to blood flow. This resistance appears to force the heart of the fetus to work harder. This could result in an increased chance of the individual developing heart disease as an adult. A group of hormones known as glucocorticoids affects the development of all the tissues and organ systems. One of the things this group of hormones does is to alter cell function by changing the structure of cell membrane receptors.
Discuss the importance of the placenta in the development of a healthy fetus. In your answer, be sure to:
• identify two factors that could influence the nutrients that can pass from the mother to the fetus [1]
• identify the group of hormones that alter cell membrane receptors and explain how this alteration can affect cell function [1]
• state the role of the uterus in the development of the fetus and the placenta [1]
The student’s response to the bulleted items in the question need not appear in the following order.
• 13 Allow 1 credit for identifying two factors that could influence the nutrients that can pass from the mother to the fetus. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — diet of the mother
• — hormones
• — blood supply to the placenta
• — the ability of the placenta to sense nutrients
• — concentration of nutrients in the blood/blood vessels
• — permeability of the placenta
• — improper functioning of the placenta
• — illness/disease
• — size of molecules
• 14 Allow 1 credit for identifying the group of hormones that alter cell membrane receptors and for explaining how this alteration can affect cell function. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Glucocorticoids–Receptors have a specific shape that determines their function. If the shape of a receptor is altered, it might not be able to perform its job appropriately.
• — Glucocorticoids–They alter cell function by changing the structure of the cell membrane receptors.
• — Glucocorticoids–They alter receptors to help them function.
• 15 Allow 1 credit for stating the role of the uterus in the development of the fetus and the placenta.
• Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The uterus is where the placenta forms and the fetus develops.
• — provides protection
All organisms need to reproduce for the continuation of their species. Discuss the process of reproduction in humans. In your answer, be sure to:
• identify one hormone present in a female that is involved in regulating the reproductive cycle [1]
• state one way the nucleus of a sex cell is different from the nucleus of a body cell [1]
• state how the normal chromosome number for humans is maintained from one generation to the next [1]
• identify one action by the mother that can influence the development of the embryo and state a result of that influence [1]
The student’s response to the bulleted items in the question need not appear in the following order.
• 16 Allow 1 credit for identifying one hormone present in a female that is involved in regulating the reproductive cycle. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — progesterone
• — estrogen
• — LH
• 17 Allow 1 credit for stating one way the nucleus of a sex cell is different from the nucleus of a body cell. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — It has half the normal chromosome number/half of the genes.
• — Sex cells are haploid/monoploid.
• — 23 chromosomes in sex cells, 46 in body cell
• 18 Allow 1 credit for stating how the normal chromosome number for humans is maintained from one generation to the next. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The egg and sperm each have half the normal chromosome number, and when they join, it restores the normal number for the species.
• — through the process of gamete production and fertilization
• — Each parent contributes half of the chromosomes.
• 19 Allow 1 credit for identifying one action by the mother that can influence the development of the embryo and stating a result of that influence. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Alcohol use can lead to Fetal Alcohol Syndrome.
• — Smoking can lead to low birth weight.
• — Poor nutrition can lead to underweight babies.
• — Drug use can lead to birth defects.
• — Good nutrition can lead to a healthy baby.
• — Drinking alcohol puts the embryo at risk.
• — Proper prenatal care might detect potential problems early so they can be treated.
Scientists have learned that when a pregnant woman smokes, one of the chemicals absorbed, nicotine, can narrow the diameter of her blood vessels that lead to the placenta. Explain why narrowing the diameter of these blood vessels can result in low birth weight babies. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The amount of food that can pass from these vessels to the placenta and to the embryo will
• be less than if the vessels are normal in diameter.
• — Less food and oxygen will reach the embryo.
• — The developing embryo will not receive enough food for normal development since not as
• much blood will flow through the placenta.
